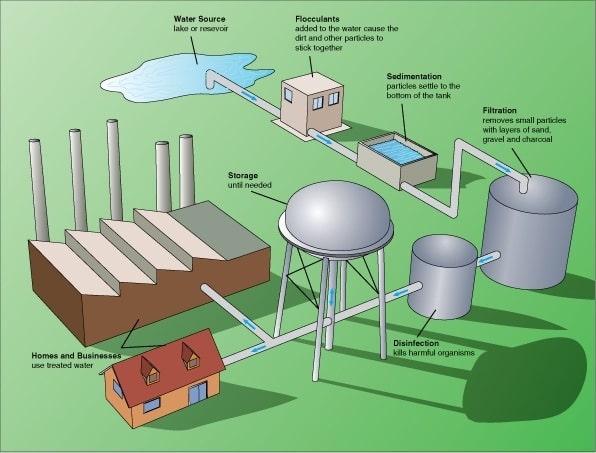
Wastewater Treatment Plant
- It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature.
- However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
- Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e.g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks).
- Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
- Wastewater is drained to the WWTP by gravity through the main sewer system of the size of a car. Having such size, objects you could hardly imagine reach the WWTPs, ranging from mattresses, fridges, tree branches to wallets disposed of by thieves in order to get rid of the evidence.
- The first mechanical stage is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment.
- Water flows through gravel chamber for settling out the grit from water. Afterwards, gravel is disposed of at the dump. Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater. At first come the coarse screens and then the fine screens which remove smaller objects such as matches, cigarette butts or undigested foods.
- After the removal of large objects, grit is to be removed from the wastewater. Similar to the gravel chamber, grit chamber allows the settlement of grit. Then, grit is removed from the tank and disposed of at the dump. Neither gravel nor grit can be reused due to their high contamination.
- The next sedimentation stage is called primary treatment during which the wastewater flows to so-called "pre-settling basins” or, using the technical term, primary settling tanks.
Bio Culture Manufacturing
- Reduces the BOD, COD & suppresses the foul odor from the STP & ETP
- Achieve COD reduction of 80-90%.
- No structural changes are necessary for implementation of bio-culture.
- Enhance the overall efficiency of plant.
- Reduce the overall chemical consumption.
- Reduction in aeration requirement, electricity requirement is reduced by 10-30%.
- Helps in smooth and efficient commissioning of the plant.
- Prevents the proliferation of pathogens.
- Eliminate the foul smell.
- Easily converts the organic waste into organic fertilizer.
- Helps in maintaining the sufficient amount of MLSS in aeration tank, which in turn increases the efficiency of the plant.
- Reduces the overall cost of operation.